 |
MolSSI Integral Reference Project
|
 |
MolSSI Integral Reference Project
|
The Gaussian Product Theorem (GPT) states that the product of two gaussians G1,G2 can be represented as a third gaussian G3 with a center a line connecting G1 and G2. This theorem is used extensively in quantum chemistry to simplify integrals.
MIRP contains functionality to compute some of the terms from the GPT which will be used within integral kernels.
Given two gaussians 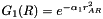 and
and 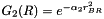 centered on
centered on 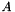 and
and 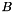 , respectively, and with
, respectively, and with 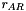 and
and 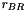 representing the distance between the center of the gaussian and a given point
representing the distance between the center of the gaussian and a given point 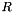
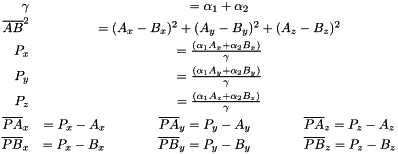
In MIRP, the parameters to the Gaussian Product Theorem can be calculated via the following functions:
 1.8.13
1.8.13